KUKA KRC2 control cabinet KPC ed05 host 00-132-566 maintenance
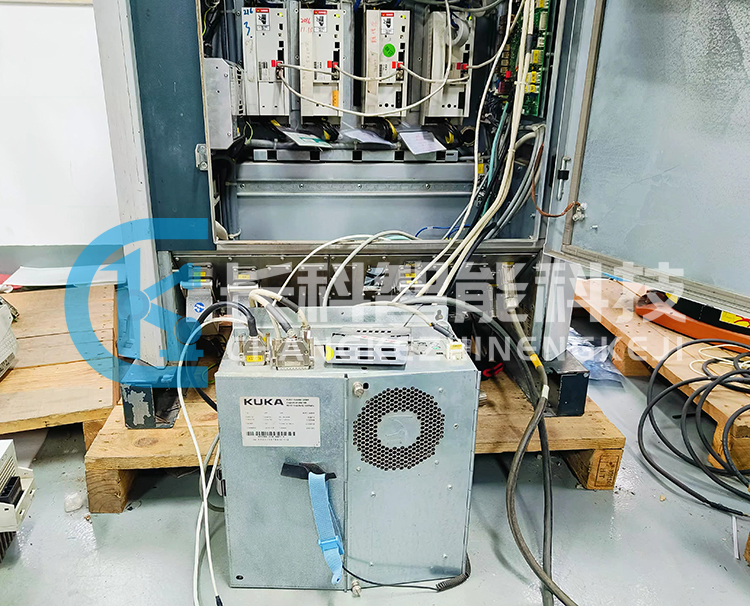

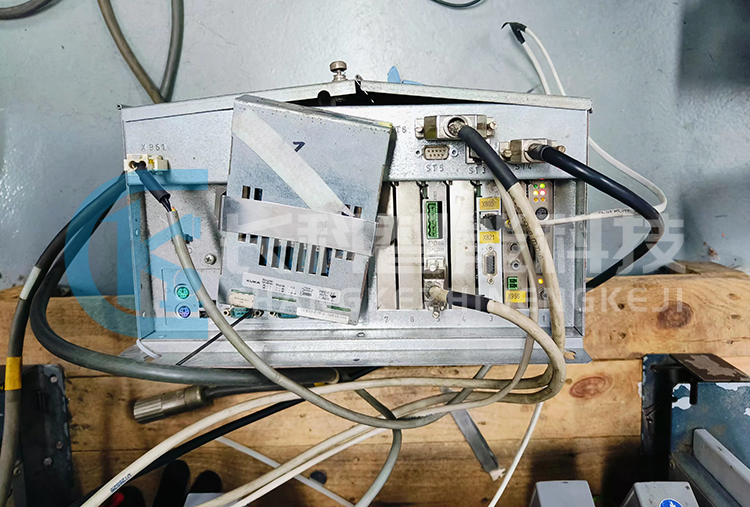

KPC stands for KUKA ControlPC (KUKA Control System Computer)
Function: KPC (KUKA PC) performs all functions of the robot control system through its various plug-in components.
1. Windows operating interface with visualization and input functions;
2. Generation, revision, archiving, and maintenance of programs;
3. Process control;
4. Trajectory planning;
5. Control of driving circuit;
6. Monitoring;
7. Components of electronic safety circuits;
8. Communicate with peripheral devices (other control systems, main computers, various PCs, networks).
The spare parts for the control system PC are as follows:
1. Motherboard with interface;
2. Central processing unit and main memory;
3. Hard drive;
4. MFC3;
5. KVGA;
6. DSE-IBS-C33;
7. RDW;
8. Battery;
9. Optional device components, such as fieldbus cards.
The central processing unit consists of two independent processor cores (Intel dual core).
In addition to running three additional controller related instance libraries on each processor core, there is also an independent secure instance library running.
Core 1: VxWorks, Windows, Safe A
Core 2: RC (Robot Control), Safe B
KPC with motherboard D2608-K:
Fujitsu brand industrial bus customized for KUKA;
Intel dual core central processing unit technology, equipped with a 2.8 GHz dual core;
DDR2 memory;
KPC with motherboard D3076-K:
Fujitsu brand industrial bus customized for KUKA;
New CPU base (LGA1155);
DDR3 memory;
Dual core processor with integrated graphics card
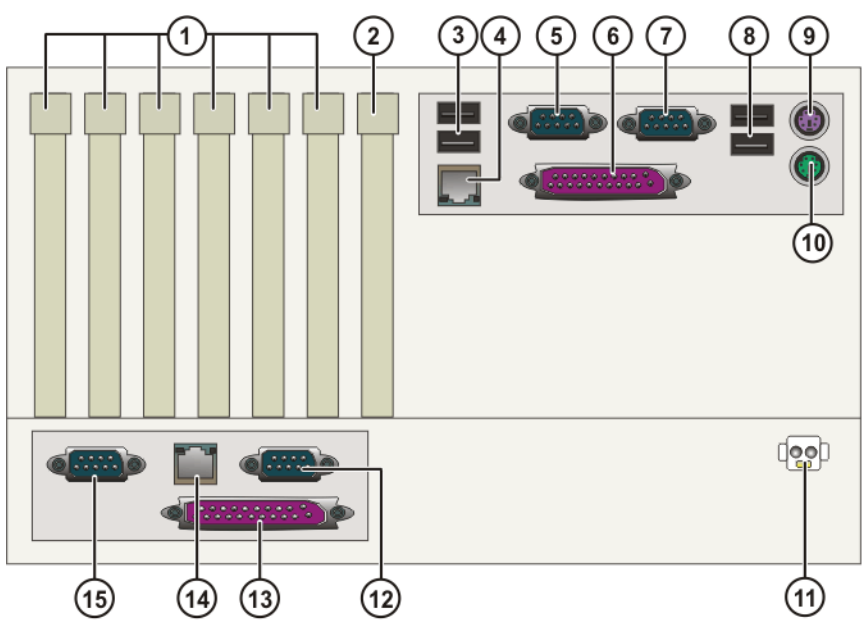
Kuka host KPC interface:
1. PCI sockets 1 to 6;
2. AGP PRO graphics card socket;
3. Two USB ports;
4. X804 Ethernet;
5. COM 1 serial interface;
6. LPT1 parallel interface;
7. COM 2 serial interface;
8. Two USB ports;
9. Keyboard interface;
10. Mouse interface;
11. X961 24V DC power supply;
12. ST5 serial real-time interface COM 3;
13. ST6 ESC/KCP (Electronic Safety Circuit/Library Card Operation Panel), etc;
14. ST3 driver bus of KPS600;
15. ST4 serial decomposer to digital converter (RDW) interface X21.
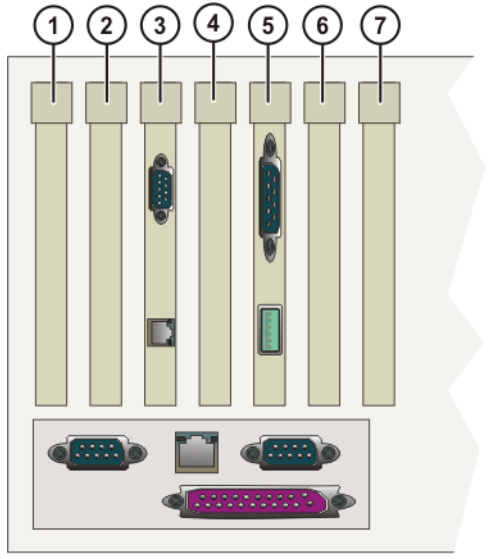
PCI slot:
Slot 1:
① Contact Bus Card (LWL Fiber Port) (Option)
② Contact Bus Card (Copper Port) (Option)
③ LPDN scanner card (option)
④ Profibus Master/Slave card (option)
⑤ CN-EthernetIP card (option)
Slot 2: LPDN scanner card (option);
Slot 3: KVGA graphics card;
Slot 4: DSE-IBS-C33 sound card (option);
Slot 5: MFC3 device card.
Slot 6:
① Network card (option);
② LPDN scanner card (option);
③ Profibus Master/Slave card (option);
④ LIBO-2PCI port card insertion (option);
⑤ Kuka router card (option).
Slot 6: Vacant Backup
KUKA KRC2 control cabinet KPC ed05 host 00-132-566 common faults:
1. Fault phenomenon: The system crashes or keyboard input cannot be performed during boot up.
Reason: The motherboard is damaged.
2. Fault phenomenon: The system continuously performs restart operations.
Reason: ① The memory module is damaged.
② The KVGA graphics card is damaged.
③ The servo drive (KSD) is damaged.
3. Fault phenomenon: BIOS malfunction displays "CMOS Checksum Error" (COMOS checksum error)
Reason: ① The lithium battery on the motherboard is in a low voltage state.
② The CMOS memory on the motherboard is damaged.




